Ninety-three years ago, confectionery giant Mars opened its first factory in Europe in Slough, England, churning out the Mars bar from a rented facility. More than nine decades later, the family-owned American business now operates 24 factories across 10 European Union countries and exports to 100 markets across the world.
Claim 70% Off TipRanks Premium
- Unlock hedge fund-level data and powerful investing tools for smarter, sharper decisions
- Stay ahead of the market with the latest news and analysis and maximize your portfolio's potential
However, Mars is not resting on its laurels, as it seeks to further expand its production capacity in Europe. On Wednesday, the company, which makes the popular Snickers chocolate bar and the candies M&M and Skittles, announced its intention to spend over €1 billion ($1.2 billion) by the end of next year to boost its operations in the EU region.
‘We Believe in Europe’
Mars said that with the new investment, it wants to expand its manufacturing capabilities, decarbonize its production value chain, and ramp up its local partnerships in the region (from farmers and suppliers to tech providers).
“We take a long-term view – we believe in Europe and we would like to see more growth for the benefit of consumers in the EU economies,” said Claus Aagaard, Mars’ chief financial officer.
The new investment builds on over €1.5 billion ($1.8 billion) that Mars has committed over the last five years to modernize its facilities, increase its production capacities, and reduce its carbon emissions in the region.
Mars Hits a Rock
However, the new investment comes as Mars is facing a key challenge in its expansion drive.
Since at least August 2024, the candy maker has been seeking to buy out competitor Kellanova (K), which makes the popular salty snacks Pringles and breakfast cereals Kellogg’s. Mars’ offer of $36 billion, plus debt for Kellanova, makes it one of the largest ever in the packaged foods industry. The offer even surpasses the American company’s acquisition of Wrigley for about $23 billion in 2008.
However, while the Kellanova deal has passed competition rules scrutiny in the U.S., European regulators are worried about the possible impact of such a large acquisition on competition among packaged food producers in the region.
The ultimate concern is the consequences on retail pricing, as a merger will give more bargaining power to Mars. Hence, they are investigating the deal and are expected to reach a conclusion by October 31.
Mars Faces Competition at Home
According to Statista data, Mars, whose net sales ran into about $25 billion as of February 2025, is the second-largest confectionery company in the world. It trails after American rival Mondelez International (MDLZ), maker of the Oreo chocolate sandwich cookie. Mondelez holds the top spot with about $36 billion in sales during the same period.
If Mars successfully merges with Kellanova, their combined capacity will top Mars’ U.S. market share of the snacking and candy industry to about 12%, according to retail data provider NielsenIQ. However, even with this merger, Mars will still need to contend with rivals such as PepsiCo (PEP), Kraft Heinz (KHC), and Hershey (HSY), among others.
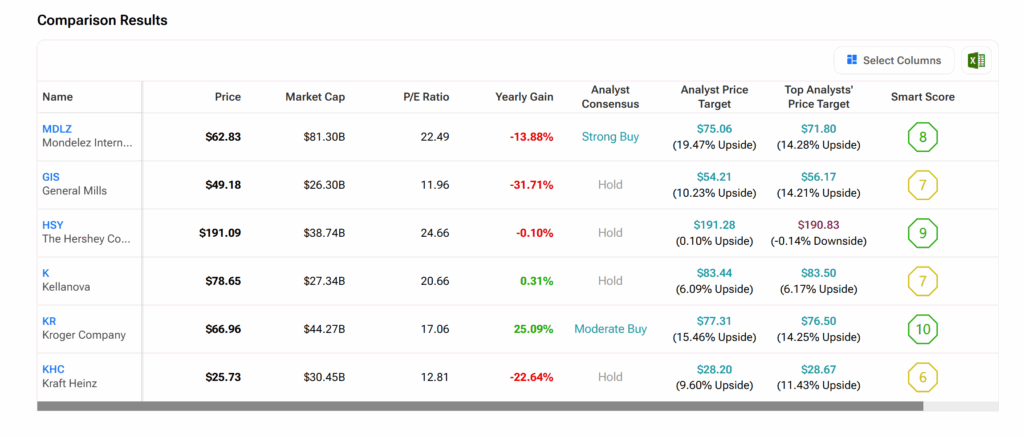
What are the Best Confectionery Stocks to Buy?
With several producers in the confectionery industry, determining which of the stocks is the best buy is essential. TipRanks’ Stock Comparison tool, as the graphics below show, provides insight into which of the stocks mentioned in this article can make for a good investment.